Blueprint Balsa Wood Glider Plans PDF⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of building balsa wood gliders using readily available PDF blueprints. Discover various designs‚ from simple beginner models to more advanced configurations. Learn essential techniques and troubleshooting tips for successful construction.
Finding Free Balsa Wood Glider Plans
The internet offers a treasure trove of free balsa wood glider plans in PDF format. Websites dedicated to model airplane enthusiasts often host a large collection of these plans‚ ranging from simple designs ideal for beginners to more complex models for experienced builders. Many plans are accompanied by detailed instructions‚ diagrams‚ and even material lists‚ making the building process straightforward. However‚ it’s crucial to carefully review the plan specifications before starting construction‚ ensuring you possess the necessary skills and tools. Remember to check the file size and format compatibility with your printer or cutting plotter. Some plans might require specific software or access permissions. Always prioritize plans from reputable sources to guarantee accuracy and safety. Online forums and communities dedicated to model airplane building can also be valuable resources‚ providing additional support and insights from experienced hobbyists. Searching for terms like “free balsa wood glider plans PDF‚” “simple glider plans‚” or “beginner HLG plans” will yield a plethora of results. Remember to download only from trusted sources to avoid potential issues with viruses or malware.
Popular Online Resources for Glider Plans
Numerous online platforms cater to model airplane enthusiasts seeking balsa wood glider plans. Websites like AeroFred Model Airplanes Plans offer a diverse selection‚ often categorized by skill level and design complexity. These sites frequently feature user reviews and ratings‚ helping you choose suitable plans. Many platforms also provide forums or communities where builders share experiences‚ tips‚ and modifications. Remember to check the file format and size compatibility before downloading. Some websites specialize in specific glider types‚ such as hand-launched gliders (HLGs)‚ while others offer a broader range of designs. Consider exploring online model airplane retailers; many provide free plans as a promotional tool or as part of their product offerings. Don’t overlook the potential of dedicated hobbyist forums and online communities. These often feature threads dedicated to sharing self-created or modified plans‚ allowing for a greater level of customization and unique designs. Always verify the legitimacy and safety of any downloaded files before opening them on your computer. Cross-referencing multiple sources for the same design can enhance the accuracy of your build;
Understanding Balsa Wood Glider Dimensions
Accurate interpretation of balsa wood glider dimensions is crucial for successful construction. Blueprint plans typically specify measurements in millimeters or inches‚ detailing wingspan‚ chord (wing width)‚ fuselage length‚ and tail dimensions. Understanding these measurements ensures proper scaling and accurate part cutting. Pay close attention to the scale indicated on the plan; some might be presented as full-size templates while others require scaling up or down. Precise measurements are particularly important for critical components like the wing airfoil‚ affecting the glider’s aerodynamic performance. Incorrect dimensions can result in instability‚ poor flight characteristics‚ or even structural failure. Using accurate measuring tools‚ such as rulers‚ calipers‚ and protractors‚ is vital. Double-checking measurements against the plan before cutting is a recommended practice to minimize errors. Consider using templates or pattern making techniques for consistently accurate cutting of multiple identical parts. For advanced designs‚ understanding the relationship between wing area‚ aspect ratio‚ and other aerodynamic factors will enhance performance. Online resources and model airplane building guides offer further insight into interpreting plan dimensions and their impact on the glider’s flight.
Essential Tools and Materials for Construction
Constructing a balsa wood glider from PDF plans requires specific tools and materials. Balsa wood sheets of varying thicknesses (1/16″‚ 1/8″‚ 3/32″) are fundamental‚ with the choice depending on the plan’s specifications. A sharp hobby knife or scalpel is essential for precise cutting‚ complemented by fine-grit sandpaper for smoothing surfaces and refining shapes. Wood glue‚ specifically designed for balsa wood‚ is crucial for strong and reliable joints. A ruler or measuring tape ensures accurate cutting and assembly‚ while a protractor aids in achieving correct angles. Depending on the design‚ additional materials might include carbon fiber rods for reinforcement or lightweight balsa wood spars for wing support. For more intricate designs‚ clamps or weights might be necessary to hold parts together during drying. Optional tools include a sanding block for even sanding‚ a hobby saw for cutting larger pieces‚ and a pin vise for drilling small holes if required by the plan. Consider using a cutting mat to protect your work surface. Remember to select a well-ventilated area for working with balsa wood and wood glue‚ adhering to safety guidelines.
Step-by-Step Building Instructions⁚ Cutting and Shaping
Begin by carefully printing the PDF glider plans at the correct scale. Using a sharp hobby knife or scalpel‚ precisely cut out each individual component from your balsa wood sheets‚ following the outlines on the printed plan. Pay close attention to detail and ensure clean cuts to maintain the glider’s structural integrity. For curved sections‚ use a combination of careful cutting and sanding to achieve the desired shape. Sanding is crucial for creating smooth surfaces and eliminating any rough edges. Start with coarser sandpaper and gradually move to finer grits to achieve a professional finish. Remember to sand in the direction of the wood grain to avoid damaging the balsa. If the plans specify any tapering or shaping of components‚ carefully follow these instructions‚ using the sandpaper and your hobby knife to create smooth transitions. Precision is key during this phase; careful work now will lead to a better-flying and more aesthetically pleasing glider. Take your time and avoid rushing‚ as inaccuracies at this stage will be difficult to correct later. Regularly compare your cut and shaped pieces against the plan to ensure accuracy throughout the process.
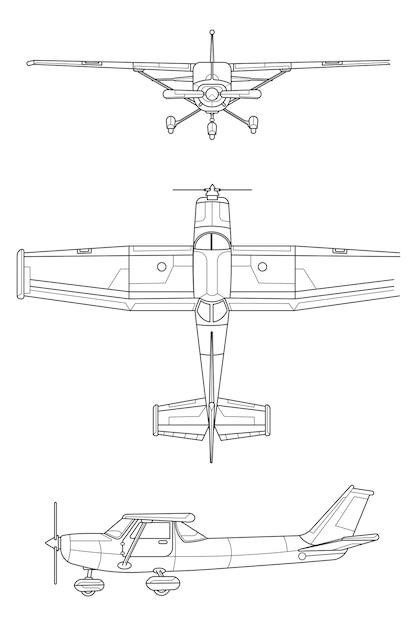
Step-by-Step Building Instructions⁚ Assembly and Gluing
With all the balsa wood components accurately cut and shaped‚ the assembly process begins. Apply a thin‚ even layer of appropriate wood glue to the designated joining surfaces‚ ensuring complete coverage. Carefully align the components as indicated on the plans‚ using clamps or weights as necessary to maintain proper alignment during drying. Avoid using excessive glue‚ as this can lead to a messy finish and potentially weaken the structure. Allow sufficient drying time for the glue to fully cure; this timeframe varies depending on the glue type and ambient conditions. For added strength‚ consider reinforcing joints with small pieces of lightweight balsa wood or thin strips of balsa‚ adding further stability to the structure. If the plans call for specific techniques like scarf joints or butt joints‚ carefully follow the instructions provided. Once the glue has set‚ check for any gaps or misalignments and make any necessary corrections. If minor adjustments are needed‚ use fine sandpaper to smooth any rough areas and ensure a seamless fit. Take your time during this process‚ as a well-assembled glider is crucial for achieving stable and controlled flight. Remember‚ patience and precision are key elements for creating a robust and well-functioning glider.
Essential Tips for Successful Glider Construction
Maintaining precision throughout the construction process is paramount. Use sharp tools to ensure clean cuts and avoid splintering the delicate balsa wood. Always work on a clean‚ flat surface to prevent accidental damage to the components. When sanding‚ use progressively finer grits of sandpaper to achieve a smooth‚ even finish. Avoid applying excessive pressure‚ which can easily damage the thin balsa wood. Accurate measurements are critical. Use a ruler or measuring tape to ensure precise dimensions. If using a template‚ trace it carefully onto the balsa wood to achieve accurate and consistent results. Before gluing‚ test fit all parts to ensure a proper fit; This will help to avoid any potential issues during the assembly process. Choose a well-ventilated area for working with glue to minimize exposure to fumes. Follow the glue manufacturer’s instructions carefully‚ ensuring proper drying time. If any errors occur during construction‚ don’t be discouraged. Balsa wood is relatively easy to repair‚ allowing for corrections. With careful attention to detail and patient execution of each step‚ you can build a high-quality glider that will perform well.
Advanced Techniques for Experienced Builders
For experienced builders seeking to enhance their glider’s performance‚ several advanced techniques can be explored. Consider incorporating carbon fiber reinforcement in critical areas like the wing spars and fuselage to increase strength and rigidity. This will improve the overall structural integrity of the glider‚ making it more durable and capable of withstanding more demanding flight conditions. Experiment with different airfoil designs to optimize lift and glide ratio. Research various airfoil profiles and their characteristics to find the best option for your glider’s intended purpose; Explore the use of lightweight balsa wood laminates for creating stronger and lighter structural components. This technique involves layering thin sheets of balsa wood together to achieve superior strength-to-weight ratios. Incorporate control surfaces such as ailerons or elevators for enhanced maneuverability. This will allow for more precise control during flight and enable you to execute more complex maneuvers. Fine-tune the center of gravity through careful weight distribution. Precise placement of the center of gravity is crucial for achieving stable and predictable flight. Experiment with different wing shapes and configurations to explore how they affect the glider’s overall aerodynamic characteristics. Explore advanced finishing techniques‚ such as applying lightweight epoxy coatings for added durability and protection. These techniques will elevate your glider’s performance and overall flight characteristics.
Troubleshooting Common Building Issues
During balsa wood glider construction‚ several common issues may arise. Warped balsa wood can be addressed by carefully clamping the affected pieces under weight until they straighten. If glue joints fail‚ ensure proper surface preparation and use a high-quality wood glue. For inconsistent wing alignment‚ carefully check the plan’s specifications and use jigs or templates for precise cutting and assembly. If the glider is too heavy‚ consider using lighter balsa wood or reducing the amount of glue used; A nose-heavy glider can be corrected by moving the battery or other components rearward. A tail-heavy glider requires repositioning heavier components forward to achieve balance. If the glider exhibits excessive instability during flight‚ the center of gravity might be incorrect. Adjust the weight distribution to achieve stable flight. If the glider experiences poor glide performance‚ adjust the wing dihedral‚ ensuring it aligns with the plan specifications. Check for any structural damage or warps that might be affecting its aerodynamic performance. Finally‚ if the glider fails to launch successfully‚ evaluate the launch technique and ensure a proper hand-launching approach. Remember‚ patience and attention to detail throughout the construction process are crucial for minimizing these issues and ensuring a successful outcome.
Recommended Balsa Wood Types and Suppliers
Selecting the right balsa wood is crucial for a successful glider build. Lightweight balsa wood‚ typically ranging from 1/16″ to 1/8″ thickness‚ is ideal for most glider designs. Consider the wood’s density; lighter wood offers better flight characteristics but requires more careful handling. Look for balsa wood with a straight grain and minimal knots for optimal strength and performance. Several online retailers and hobby shops specialize in supplying high-quality balsa wood. These suppliers often offer a variety of sizes and densities to suit different project needs. When purchasing‚ ensure the wood is appropriately stored to prevent warping or damage. Proper storage involves maintaining a consistent level of humidity to prevent expansion or contraction of the wood. Check customer reviews and compare prices before making a purchase. Consider buying slightly more balsa wood than necessary to account for potential errors or imperfections. Remember‚ using high-quality balsa wood contributes significantly to the overall strength‚ flight performance‚ and longevity of your finished glider.
Different Glider Designs and Their Characteristics
Numerous balsa wood glider designs cater to various skill levels and flight preferences. Simple designs‚ ideal for beginners‚ often feature straightforward construction and forgiving flight characteristics. These might include high-wing monoplanes with relatively large wingspans for enhanced stability. More advanced designs might incorporate swept-back wings‚ dihedral angles (upward-angled wings)‚ or even delta wings‚ each affecting flight performance differently. Swept-back wings enhance maneuverability‚ while dihedral improves stability. Delta wings offer high lift but can be less stable. Consider the glider’s intended purpose⁚ long-distance flight requires designs emphasizing lift and efficiency‚ while acrobatic maneuvers necessitate a more agile design. Some plans offer detailed specifications for wingspan‚ chord length (width of the wing)‚ and airfoil shape (cross-section of the wing)‚ parameters that significantly influence flight performance. Researching various designs helps you choose a blueprint that aligns with your building skills and desired flight characteristics. Remember that even within a specific design‚ minor adjustments can significantly impact the glider’s flight behavior.
Flying and Tuning Your Balsa Wood Glider
Once constructed‚ carefully launch your balsa wood glider. Begin with gentle tosses‚ observing its flight path. Does it glide smoothly‚ or does it veer off course‚ stall‚ or nosedive? These observations provide crucial feedback for tuning. Adjustments often involve repositioning the center of gravity (CG). A rearward CG typically leads to increased stability but potentially reduces maneuverability. A forward CG results in a more responsive but less stable glider. Fine-tune the CG by adding small weights (like tiny pieces of lead) to the nose or tail. Experiment with launch techniques; a smooth‚ level toss is ideal. Wind conditions greatly impact flight‚ so choose a calm area for initial test flights. If the glider consistently veers‚ consider slight adjustments to the wing’s angle of incidence (the angle between the wing and the fuselage). A slight upward adjustment might correct a tendency to nosedive‚ while a downward adjustment might address excessive climbing. Remember that even subtle changes can dramatically alter the glider’s flight characteristics. Through iterative testing and adjustments‚ you will refine your glider’s performance to achieve optimal stability and flight duration. Keep meticulous notes on your adjustments and their effects for future reference.


